Book Appointment Now

Understand the production process of custom aluminum and zinc die casting reveals its intricate and highly skilled nature.
This manufacturing method involves pouring molten aluminum or zinc at high pressure and speed into enduring molds crafted from hot working steel. The result is a precise and economical process that yields complex, pressure-tight components with smooth surfaces and clean edges.
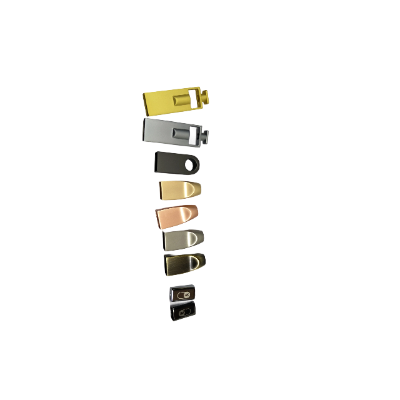
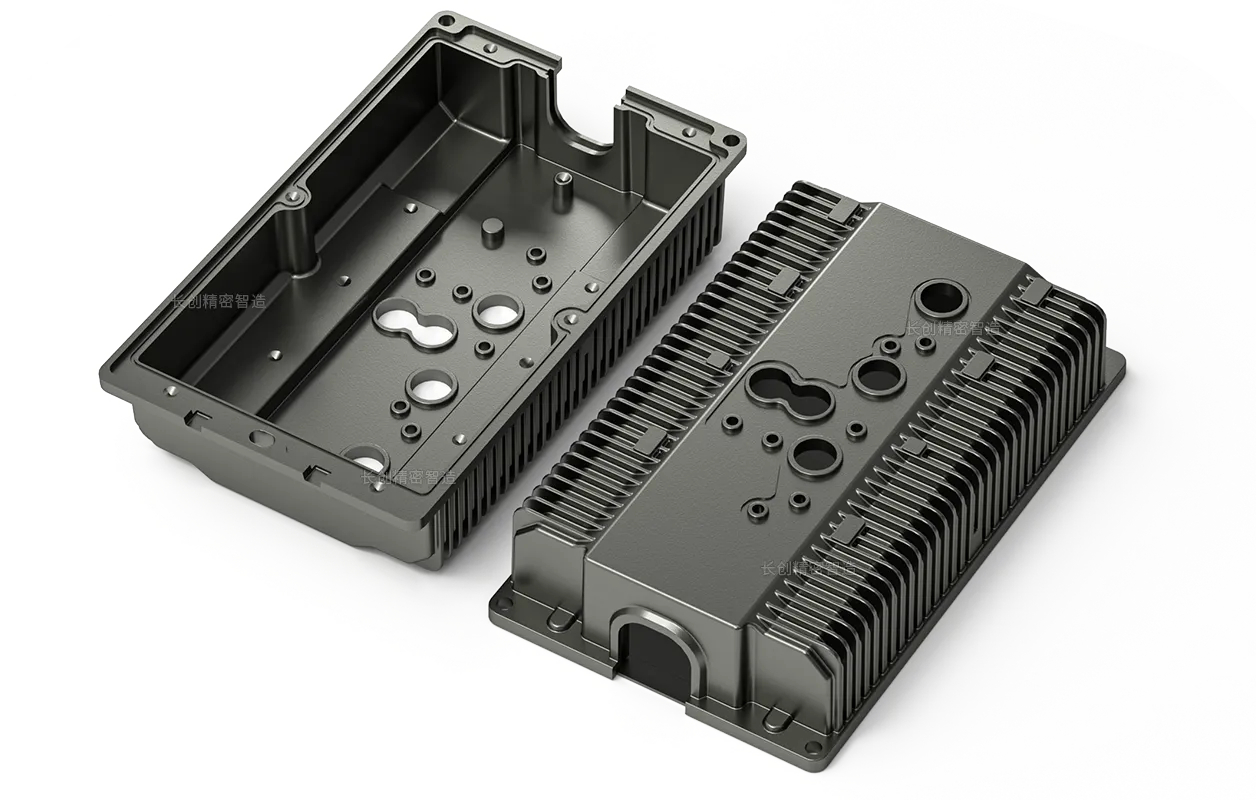
Die casting offers numerous advantages over alternative methods, such as shorter cycle times, the ability to produce complex geometries, consistent quality, and reduced material waste. It’s particularly suited for making components like transmission housings for electric motors, injection pump housings, structural parts for transmissions, carrier boards, and cooling elements used in control systems and power electronics.
At VOIT Automotive, die casting machines operate with locking forces ranging from 5,000 to 16,000 kN, handling component weights between 0.25 kg to an impressive 15 kg for final products. Unlike sand casting, which uses single-use molds, die casting employs reusable steel molds (or dies), similar to gravity die casting but enhanced for precision and durability.
High-pressure die casting involves injecting liquid aluminum or zinc into molds at pressures between 150 and 1,200 bar—remarkably higher than the 2 bar typically used to inflate a car tire. This automated process is ideally suited for high-volume and series production. The cost efficiency stems from the ability to create detailed molds, including internal complexity and external threads, without extensive secondary processing.
One of the key strengths of high-pressure die casting lies in the reusability of the molds. Depending on the alloy used, tens of thousands of castings can be produced with no degradation in quality. In fact, this process ensures exceptional uniformity and precise dimensional accuracy in each component. Because aluminum and zinc die casting alloys are iron-free, the resulting parts are versatile and fit for a broad range of applications. Additionally, the process’s capability to manufacture intricate geometries and ultra-thin components makes it especially appealing for industries demanding precision and innovation.